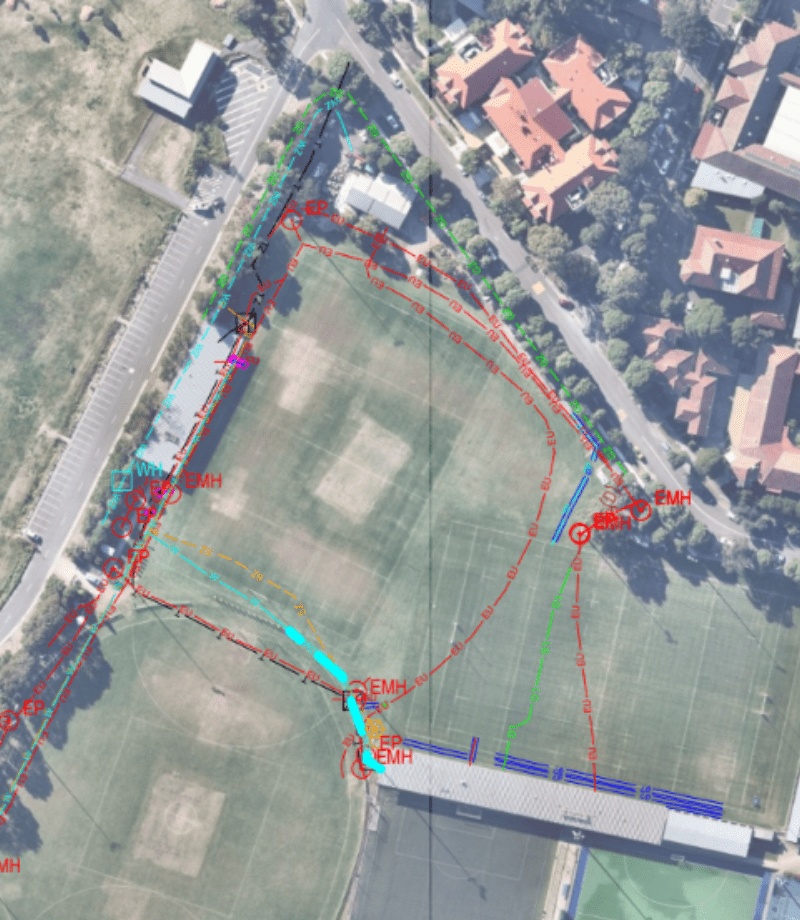

Whether you require commercial, industrial or residential locating, Ground Penetrating Radar, also known as GPR, is a geophysical surveying technique that uses reflections from radar pulses to create an image of the sub surface. This scanning technique will allow Smartscan Locators technicians to efficiently and accurately locate submerged utilities and targets that are both metallic and non-conducive. GPR reports are great for providing graphic evidence in support of your investigative findings. These reports include visual data of the asset that was located, including dimensions, depths and connecting infrastructure.
Key applications of the GPR:
Utility Mapping
Topographical Survey
Detail
Point Clouds
Set Out
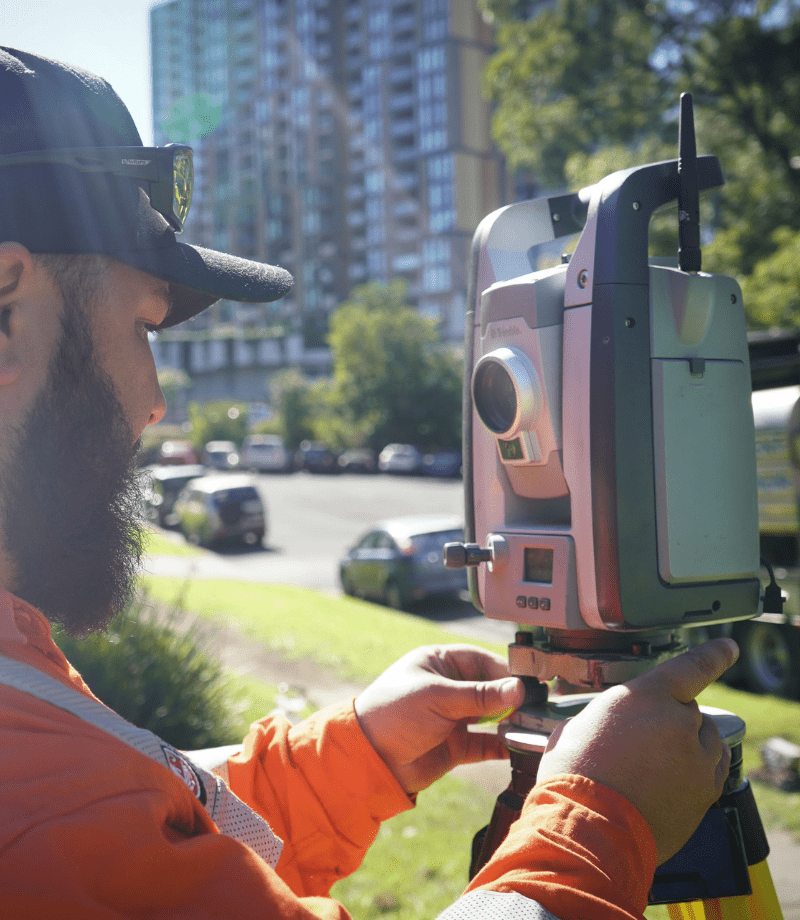
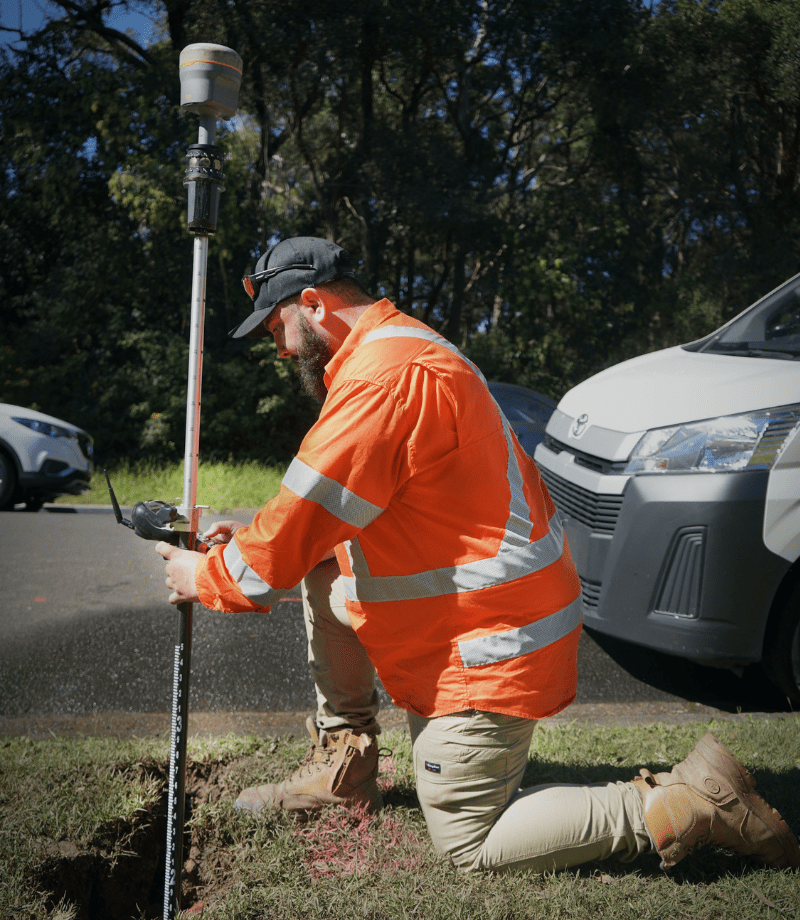


What Is Ground Penetrating Radar
Ground-penetrating radar (GPR) is a non-destructive geophysical method that uses radar pulses to create an image of the subsurface. It is commonly used to detect and map subsurface structures and features without the need for excavation or drilling.
GPR works by emitting high-frequency radio waves into the ground. When these waves encounter different materials or objects, they are reflected back to the surface, where they are detected by a receiver. The time it takes for the radar signals to return to the receiver is used to calculate the depth and density of the materials beneath the surface.
The technology is effective in a variety of media, including soil, rock, ice, and concrete, and can identify changes in material, voids, cracks, and objects like pipes and cables. The frequency of the radar waves can be adjusted depending on the required penetration depth and resolution; higher frequencies yield finer detail but shallower penetration, while lower frequencies penetrate deeper but offer less detail.
GPR’s depth of penetration varies depending on the material’s electrical conductivity and the frequency of the radar waves. It performs best in dry, low-conductivity materials and is less effective in wet or clay-rich soils.
Applications of GPR are diverse, ranging from engineering, archaeology, and environmental studies to law enforcement and military uses. It can be used to inspect the condition of infrastructure, locate utilities, define landfills, map archaeological sites, and detect buried objects like mines.
